Environment Variables & Secrets
When integrating with external services you typically store your credentials in environment variables. This is done to avoid hardcoding secrets into your codebase.
There are several environments that require different credentials, for example:
- On your local machine: Development
- Secrets on deployed Workers: Staging & Production
Development
Section titled “Development”Create a .env file in the root of your project.
SECRET_KEY = "value";API_TOKEN = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";Cloudflare uses .dev.vars, however, .env is the typical approach. Therefore, when you run pnpm dev, RedwoodSDK will automatically create a symlink from .env to .dev.vars.

Updating Types
Section titled “Updating Types”After adding any environment variables, run:
npx wrangler typesThis adds the environment variable and associated type to worker-configuration.d.ts and avoids unknown types when accessing env.
// Generated by Wrangler by running `wrangler types`// Runtime types generated with ....declare namespace Cloudflare { interface Env { SECRET_KEY: string; API_TOKEN: string; }}Production / Secrets on deployed Workers
Section titled “Production / Secrets on deployed Workers”To add a secret to a deployed worker, run:
npx wrangler secret put <KEY>Then, the CLI will prompt you to enter the secret value.
These can also be added and managed via the Cloudflare dashboard.
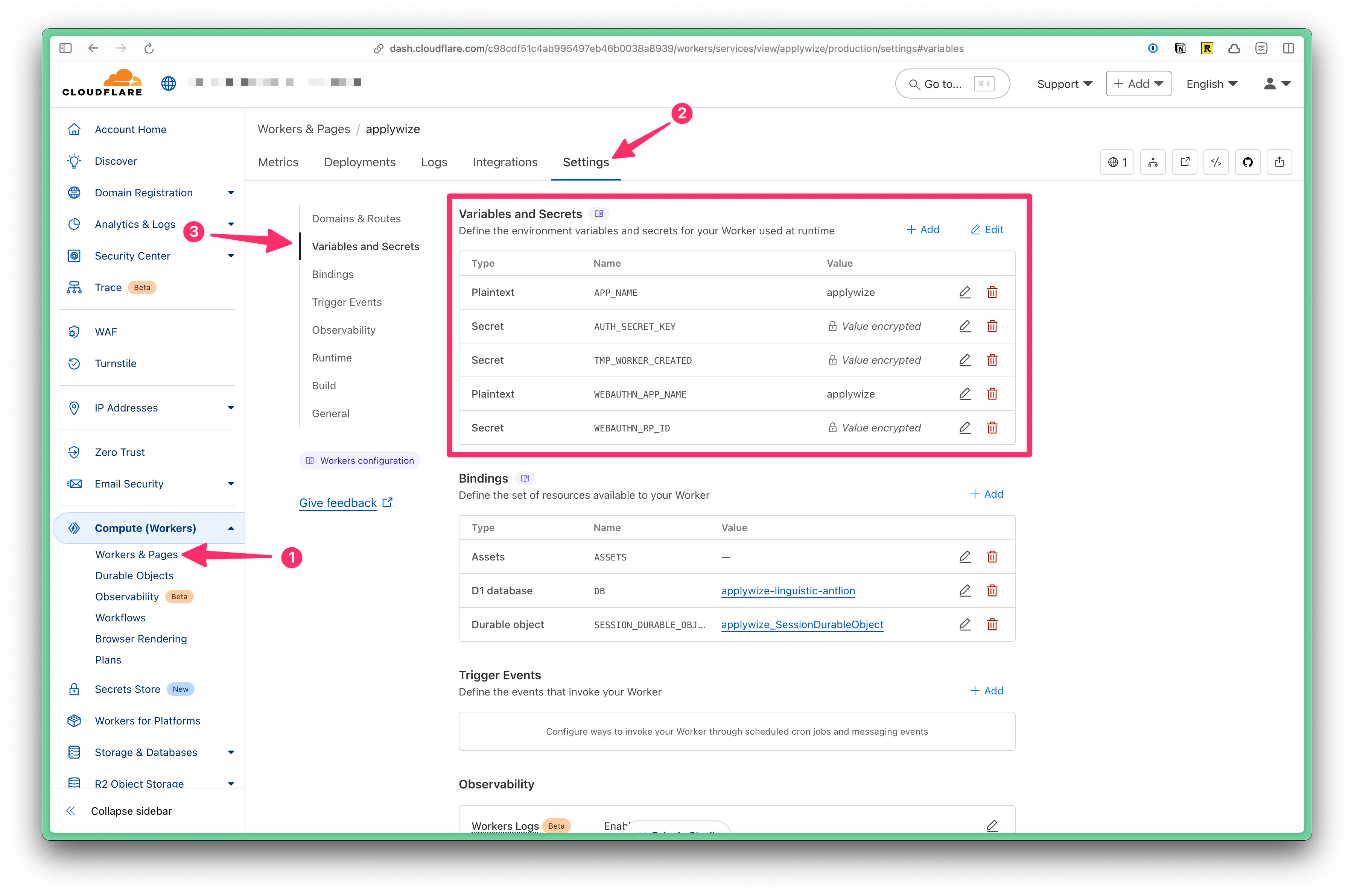
- Expand the Computer (Workers) tab
- Click on Workers and Pages
- Click on the name of the worker
- Click on the “Settings” tab
- Click on the “Variables and Secrets” section
Using an Environment Variable
Section titled “Using an Environment Variable”At the top of your file, import env:
import { env } from "cloudflare:workers";Then, you can access the environment variables through the env object.
const rpID = env.WEBAUTHN_RP_ID ?? new URL(request.url).hostname;Managing staging and production configurations
Section titled “Managing staging and production configurations”Define each Cloudflare environment in wrangler.jsonc. Wrangler reads the env block to decide which variables, routes, and bindings to apply when you deploy with CLOUDFLARE_ENV.
{ "name": "redwood-example", "main": "./dist/worker.mjs", "compatibility_date": "2024-10-21", "env": { "staging": { "vars": { "APP_BASE_URL": "https://staging.example.com" }, "routes": [ { "pattern": "staging.example.com/*", "custom_domain": true } ] } }}After updating wrangler.jsonc, run pnpm generate to update the generated type definitions.
Create environment-scoped secrets with the --env flag:
npx wrangler secret put DATABASE_URL --env stagingDeploy with CLOUDFLARE_ENV=staging to load the staging configuration, or omit it to deploy the default production configuration.